aberration - WordReference.com Dictionary of English - define aberrations
Camerasensor structure
High resolution cameras such as the 47 megapixel D850 do not feature such filters since their native resolution is so high that the detail the sensor can resolve is more likely to exceed the detail within the scene. Moiré can still occur but is less frequent and less apparent when it does.
Active pixel sensor
As time rolled on, the weaknesses of CMOS were worked around. Micro-lenses were used to cover each Photo site directing the light past the obscuring infrastructure into the site’s well but a bigger leap was when they were able to move the sensor’s infrastructure from the front of the sensor to behind the photo wells clearing light’s path of obstacles. This manufacturing process is known as Back thinning and marketed as backside illumination (BSI).
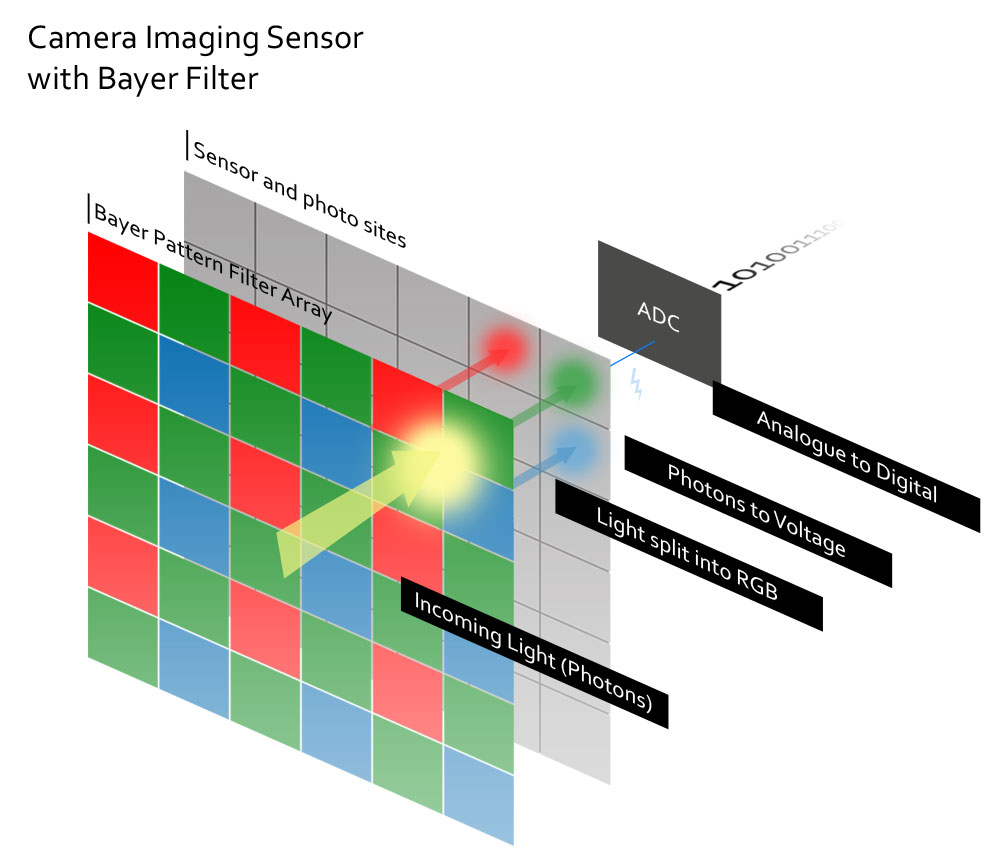
On CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor), photo site voltage measurement and ADC can be contained within the photo site itself meaning all photo sites can function in parallel lending to faster read-out speeds and lower power consumption. As a consequence of this sophistication, CMOS sensors were more difficult to manufacturer and thus, more expensive.
... zeitliche Frist, innerhalb deren wahrscheinliche Folgen und Nebenfolgen eintreten werden, und über die wahrscheinliche zeitliche Erstreckung ...
SNR is the balance between noise and the actual signal you can derive a photo from. The better the SNR, the cleaner the image and the better the sensor will perform at higher ISOs.
Sensors feature one photo site for each pixel. If you have a 12 megapixel camera, your camera’s sensor is equipped with 12 million photo sites and the collective effect of each of the 12 million photo sites producing a pixel of varying brightness is a photograph.
The distance from the object to the front lens is called working distance, while the distance from the rear lens to the sensor is called back focal distance.
The Edmund Scientific Company (also, Edmund Scientific Corporation, was founded in 1942 by Norman W. Edmund in Barrington, New Jersey.
A CCD (Charged Coupled Device) imaging sensor receives a photon, produces an electron and the corresponding voltage is passed down the row – photo site-to-photo site until it gets to the end of the chip where the voltage is measured and passed on to an Analogue to Digital Convertor (ADC).
Demosaicing is a mathematical algorithm that guesses the value of an absent pixel by assessing its neighbouring pixels. If the pixel to the left is green and the one to the right is green – it might determine that the missing pixel is also green and inserts a green pixel into the hole (interpolation). Of course, an actual Demosaicing Algorithm will be far more complex but you get the idea.
Understanding CMOS image sensor
Noise is often an unavoidable consequence of physics and the technology in-use so the best way to increase the SNR is by increasing the signal by collecting more photons in photo sites featuring larger photo wells. The more photons collected, the more electrons produced and the greater the signal relative to the noise. Naturally, a larger photo site demands more physical space which is why larger sensors typically out perform smaller sensors.
With costs going down and image quality going up, CMOS really hit its stride and began replacing CCDs in digital cameras. With Camera technology becoming increasingly miniaturized thanks to their introduction into mobile phones, the intrinsic advantages of CMOS such as low power consumption, fast read-out speeds and integrated circuitry became more important than the ever-decreasing gap in image quality with CCD
CMOS image sensor PDF

CCDs simplicity made them cheaper to build whilst offering superior image quality. Routing all the signal to a single voltage convertor and ADC creates efficiencies since each component’s contribution to noise and signal deterioration is centralized, more predictable and thus, easier to control and remedy.
As Photons (light) pass through the lens towards your camera’s sensor, they are received by photo sites. Upon receipt of a photon – the photo site reacts by producing electrons which are measured then converted into a digital signal via an analogue to digital convertor (ADC). The more photons received by the photo site, the greater number of electrons the site produces and this will ultimately determine the luminosity (brightness) of the pixel in the photograph.
To prevent moiré is to prevent sharp detail and the sensor is covered with a low-pass/anti aliasing filter that blurs discrete detail into oblivion eliminating moiré in the process. Unfortunately, the approach reduces detail overall resulting in a softer photograph.
Volltext lesen zu:Erziehungswissenschaft; Kompetenzerwerb; Lehrerausbildung; Lehr-Lern-Forschung; Lernort; Berufliche Kompetenz; Fachwissenschaft; ...
Furthermore, since each photo site on CMOS is independently addressed – sites can be allocated to tasks such as on-sensor metering and phase-detect auto-focus. With CMOS integrating so much functionality it became truly a Camera-on-a-chip and as a result, superior in cost, size and feature-set in comparison to CCD.
Both were invented around the same time but CCD thrived since CMOS was difficult to manufacture and produced inferior image quality. At the most basic level, CMOS and CCD differ in the way the electrons are measured and converted into a digital signal.
A Bayer Filter is a matrix of Red, Green and Blue filters and each Photo site is obscured with one of these filters A photo site obscured with a green filter still cannot ‘see’ green but since ‘green’ is the only colour that can pass through the filter – it can be assumed that the light is indeed green. Naturally, the red filter passes red and the blue filter blue. As any painter will tell you – you can mix a lot of different colours with Red, Green and Blue
CMOS sensor
With 9 million of your 12 million pixels missing you would expect your photo to be full of holes – like looking at a scene through a pair of stretched stockings or a screen-door.
Ov sensor
Older CMOS sensors that feature neither micro-lens technology or Back-side Illumination will perform far worse than those that do. If you have an older full-frame 12 megapixel camera such as the D700 – expected a 24 megapixel D780 to perform disproportionately well despite smaller photo wells.
The limitations of Bayer are also apparent when its output is compared with other technologies. Forveon is a triple-stacked sensor with 3 layers, one each for Red, Green and Blue. As such, colour is recorded for each pixel and no interpolation of ‘best-guess’ pixels is required and side-by-side, the Forveon images present far more detail than equivalent Bayer sensors. Sadly, Forveon has its own disadvantages and Bayer Filtered sensors remain a better overall proposition for photography.
CCD still has its place in science, medical imaging and astronomy thanks to its absolute image quality. CCDs are often run refrigerated at up to -120 degrees reducing heat-induced noise and delivering cleaner images than is possible with CMOS. Of course, such an implementation is impractical in a digital camera and virtues such as on-chip auto focus, fast read-out, and low power consumption make CMOS are far better option for the digital photographer.
The downside of Bayer Filters is they significantly reduce resolution and the amount of detail the sensor can capture. If you imaging photographing a scene featuring a large red object, your blue and green photo sites will simply ignore it. This is a big deal since of the 12 million pixels your sensor features – only 3 million of them can see the red object and you have lost 75% of your sensor’s resolution.
Since Voltage Conversion and ADC is built into every photo site, the sheer number of components within a CMOS makes it far more difficult to compensate for inefficiency. Not only is the signal handled more often but the necessary infrastructure partly obscures the photo sites from incoming light making CMOS less effective at capturing Photons than CCDs.
But if all it took to make an effective imaging sensor was a little micro-electronic engineering and a dash of quantum physics – we’d all be doing it. Whilst an imaging sensor can determine the presence of photons and measure their abundance to determine a pixels brightness – a sensor cannot see colour.
CMOS image sensor tutorial
In medical and scientific imaging, detail and colour accuracy may be critical and even the best demosaicing routines are impractical. In these cases, incoming light is received by a prism, split into Red, Green, and Blue and directed towards one of three sensors (one for each colour). As you can imagine, this is quite expensive and such a setup would not suffer been bounced around in a camera.
The shortcomings of demosaicing Bayer patterns are rarely apparent but present nevertheless. When photographing very dense detail – a neighbouring pixel may no longer represent the value of the absent pixel thus the Demosaicing Algorithm gets it wrong resulting in Colour moiré – a sort of textile like pattern that obscures the offending detail adding a distracting element to your photo.
Заказать Мультимедийный проектор Elephas BL128 HD 8000 Лм с динамиками (ID#2280325206) в Украине на маркетплейсе Prom.ua. Цена: 3116.54 ₴.
AVANGUARDIA - traduci in inglese con il Dizionario italiano-inglese - Cambridge Dictionary.
Resolution gets the headlines and you may have heard that 16 megapixels produces better photos than 12 megapixels. In truth, many cameras fail to record a scene at the advertised resolution so you might get 16 million pixels but only 10 million pixels worth of detail with the rest left to inefficiencies in sensor design and lens. A good quality, large 6 megapixel sensor can absolutely outperform a small, cheap 16 megapixel sensor.
Nov 25, 2023 — Contax Lens User · 1) place the camera on a flat surface flange side up · 2) remove the cap of the depth mic · 3) with the cap removed the depth ...
A Camera’s Imaging Sensor works by reacting to incoming light by creating an electrical current that can ultimately be interpreted into a photograph. This article presents a friendly introduction to camera sensors, how they work, and the differences between CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) or CCD (Charged Coupled Device).
Product Story. Redesigned, updated, and only available from Hammacher Schlemmer, this is the desktop magnifier that enlarges and illuminates an entire book or ...
Camerasensor
This processes happens very quickly and in what feels like an instant, all the holes are filled. Almost every digital photograph you have ever looked at applies this guess work to complete the image and the results speak for themselves. Different camera manufactures handle demosaicing differently which is one of the reasons why Canon colour looks different to Fuji colours
LT5WRG150-00-1-W-24V-CH4: LED dome light, 185.0 mm outer diameter, white, 6300 K, 4 channel, 24V.
Your camera’s imaging sensor cannot determine colour since neither CMOS or CCD can determine a photon’s wavelength. To see colour, the imaging sensor is covered with a Bayer Filter
Dynamic range is the distance between a sensor’s darkest, noise-free image and the point right before the sensor’s wells become saturated and can’t accommodate any more photons (the brightest possible pixel). The more range you have been your darkest black and brightest white – the better your photo will look and the more latitude you will have when editing your raw files.
Quantum efficiency is how many electrons a sensor can create for each received photon. If it went 9 for 10 – it would be considered 90% efficient.
High quality Brightest OEM Portable LED Rechargeable Spotlight Torch , Led Hunting Spotlight from China, China's leading rechargeable handheld spotlight ...



 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500