10X Optical Zoom Digital Camera - optical camera
Fresnellens
This post might contain affiliate links. That means we will get a small fee if you make a purchase through the links, without any additional cost to you. Support Canon Watch! We love to bring you all the latest news about Canon and photography. If you buy your gear through our affiliate links you help this site going on.
Use these flashcards to help memorize information. Look at the large card and try to recall what is on the other side. Then click the card to flip it. If you knew the answer, click the green Know box. Otherwise, click the red Don't know box.
Catadioptric
Make sure to remember your password. If you forget it there is no way for StudyStack to send you a reset link. You would need to create a new account. Your email address is only used to allow you to reset your password. See our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Concavemirror
If you are logged in to your account, this website will remember which cards you know and don't know so that they are in the same box the next time you log in.
When you need a break, try one of the other activities listed below the flashcards like Matching, Snowman, or Hungry Bug. Although it may feel like you're playing a game, your brain is still making more connections with the information to help you out.
Cassegrain telescope
Dobsonian telescope
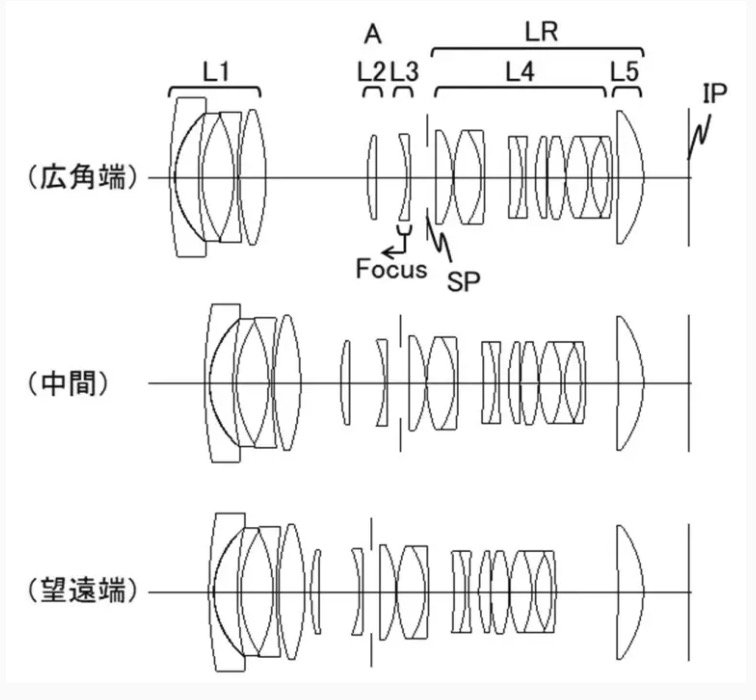
Canon patent application 2024103311 (Japan, published 08/01/2024) discusses method and optical formulas for three telephoto…
Canon patent application 2024101615 (Japan, published 7/30/2024) discusses optical formulas for two lenses: 15-28mm F2.8…
Various types of catadioptric systems are also used in camera lenses known alternatively as catadioptric lenses (CATs), reflex lenses, or mirror lenses. These lenses use some form of the cassegrain design which greatly reduces the physical length of the optical assembly, partly by folding the optical path, but mostly through the telephoto effect of the convex secondary mirror which multiplies the focal length many times (up to 4 to 5 times). This creates lenses with focal lengths from 250 mm up to and beyond 1000 mm that are much shorter and compact than their long-focus or telephoto counterparts. Moreover, chromatic aberration, a major problem with long refractive lenses, and off-axis aberration, a major problem with reflective telescopes, is almost completely eliminated by the catadioptric system, making the image they produce suitable to fill the large focal plane of a camera.
Catadioptric lenses do, however, have several drawbacks. The fact that they have a central obstruction means they cannot use an adjustable diaphragm to control light transmission. This means the lens’s F-numbervalue is fixed to the overall designed focal ratio of the optical system (the diameter of the primary mirror divided into the focal length). Exposure is usually adjusted by the placement of neutral density filters on the front or rear of the lens. Their modulation transfer function shows low contrast at low spatial frequencies. Finally, their most salient characteristic is the annular shape of defocused areas of the image, giving a doughnut-shaped ‘iris blur’ or bokeh, caused by the shape of the entrance pupil. Patent JP-A-2017-219642 discusses such a catadioptric lens. Focal length: 400 mm F No: 5.6 2 ω: 1.96 Image height: 13.66mm Back focus: 33.07mm Lens length: 247.73mm Source share share share
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. If you want to know more or withdraw your consent to all or some of the cookies, please refer to the cookie policy.By closing this banner you agree to the use of cookies.
Catadioptric lenses do, however, have several drawbacks. The fact that they have a central obstruction means they cannot use an adjustable diaphragm to control light transmission. This means the lens’s F-numbervalue is fixed to the overall designed focal ratio of the optical system (the diameter of the primary mirror divided into the focal length). Exposure is usually adjusted by the placement of neutral density filters on the front or rear of the lens. Their modulation transfer function shows low contrast at low spatial frequencies. Finally, their most salient characteristic is the annular shape of defocused areas of the image, giving a doughnut-shaped ‘iris blur’ or bokeh, caused by the shape of the entrance pupil.



 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500