360 Viewer PRO - The 360 Image Viewer and EDITOR for PC - 360 viwer
The working distance is the distance between the objective and the cover glass, or between the objective and the top (or bottom) of whatever vessel you are imaging through, when your sample is in focus. When you are imaging through something thin, like a cover glass, you can use objectives with shorter working distances. But when you are imaging samples that are in a thicker vessel, such as a plastic plate or dish, you will probably need an objective that has a longer working distance. The working distance of an objective is often written on the objective. The working distance of the objective in this example is 7.4 mm. It is considered to have an ‘extra-long working distance’ and is abbreviated as ELWD on the objective.
As a team, Advance LED Supply is dedicated to providing exceptional service and the highest quality of LED lighting products. We stay on the cutting edge of ...
Working distancedefinition microscope
The Immersion medium is what's between the objective and the coverslip (or the bottom of the dish or flask that holds your sample).
Figure 3. Use of immersion media matched to the objective can minimize the refractive index differences between the objective and the sample.
Aspheres are often used to collimate light that is leaving a fiber or laser diode. The surface of an asphere is designed to eliminate spherical aberration, as spherical aberration is often what prevents a single spherical lens from achieving diffraction limited performance when focusing or collimating light for monochromatic sources.
Lots of times, you will hear people talk about the “NA” of an objective. “NA” stands for numerical aperture and its value partly depends on the refractive index of the material that is between the objective and the glass coverslip that your sample is on. In general, objectives with higher NA give you better resolution. Higher NA objectives often have higher magnification and use some sort of immersion medium. Immersion medium is used to alter the refractive index of the space between the objective and glass coverslip so that it is closer to the refractive index of the glass coverslip itself. This minimizes refraction and loss of light, ultimately giving you a better image.
This general, non-acidic sanitizer is an effective solution for your business to combat COVID-19. Provide a safe working environment for your employees and ...
Working distancevs focal length
Figure 2. Same field of cells captured at different magnifications. Each magnification can offer different information, and the best choice for your experiment will vary depending on what you want to know.
In this article we will discuss how collimated light beams are created, lenses and coatings that can be applied to manipulate a broad spectrum of wavelengths, and practical applications.

Learn the correct magnification for your experiment and how to tell if your objective can be used with air, oil, or other immersion media.
Chromatic aberration of a single lens causes different wavelengths of light to have differing focal lengths, whereas an achromatic doublet brings red and blue light to the same focal point.
Collimated beams find practical use in various fields such as scientific investigations, laser advancements, sensors, medical imaging, and industrial processes like laser cutting and welding.
What is a working distanceofalens
There are different types of lenses used to generate a collimated beam, each with their own disadvantages and advantages. We will discuss a few options below.
To achieve collimated light, there are two theoretical methods: a) positioning an extremely tiny source precisely at a distance equal to the focal length of an optical system with a positive focal length or b) observing the point source from an infinitely distant location. In reality, neither of these situations is achievable. As well, according to diffraction theory, even if one of these conditions were met, there would still be a certain degree of spreading or divergence.
2012227 — This is a game-changer: I can now execute clean exposure pulls with Canon EF, Sony Alpha, and Lumix lenses that simply didn't allow such things ...
Working distanceof 10X objective
Numerical aperture is a property of the objective that indicates how good the resolution can be in the image you collect (basically how much fine detail you can see).
Aspheric lenses have a varying curve across the lens, whereas traditional lenses have a circular shape and could be part of a larger circle or sphere. Aspheric lenses tend to be thinner and flatter compared to their traditional lens counterparts.
To collimate a diverging beam, we can use lenses with different focal lengths. The resulting diameter of the collimated beam increases as the focal length becomes longer. Assuming an initial tight focus and the subsequent expansion of the beam over a long distance, the distance between the focus and the collimation lens should be equal to the focal length. Using this information, the radius of the collimated beam can be determined by multiplying the half-angle of the beam divergence (or more precisely, its tangent) by the distance.

To minimize divergence of a collimated beam, two factors must be balanced: focal length of the collimating system and size of the light source. The diagram below demonstrates the approximate divergence of a collimated beam:
Working distanceof 4x objective
A collimated beam is light with weak divergence, meaning it’s a flow of photonics that move in parallel to one another, without dispersing. The beam remains concentrated in a specific direction, and its energy is evenly distributed along its path. This distinct characteristic of collimated beams makes them valuable in different industries, such as scientific research, engineering, and medical applications.
In the real world, light is collimated with a collimator device, which essentially is a lens or curved mirror where the focal length or curvature radius is chosen such that the originally curved wavefronts become flat. Of course, the beam radius at the position of the lens or mirror should be large enough to obtain a low divergence. Any residual divergence can be fine adjusted via the position of the lens or mirror along the beam direction. The collimation can be checked, for example, by measuring the evolution of beam radius over some distance in free space with certain kinds of interferometers.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I1PRx9o_WSM Khaled Alweshah ... SIM-UNLOCKER PRO 8.8.9 - Multiverse Unlock Editio... ... Frp SL112C Cricket Icon5 ?

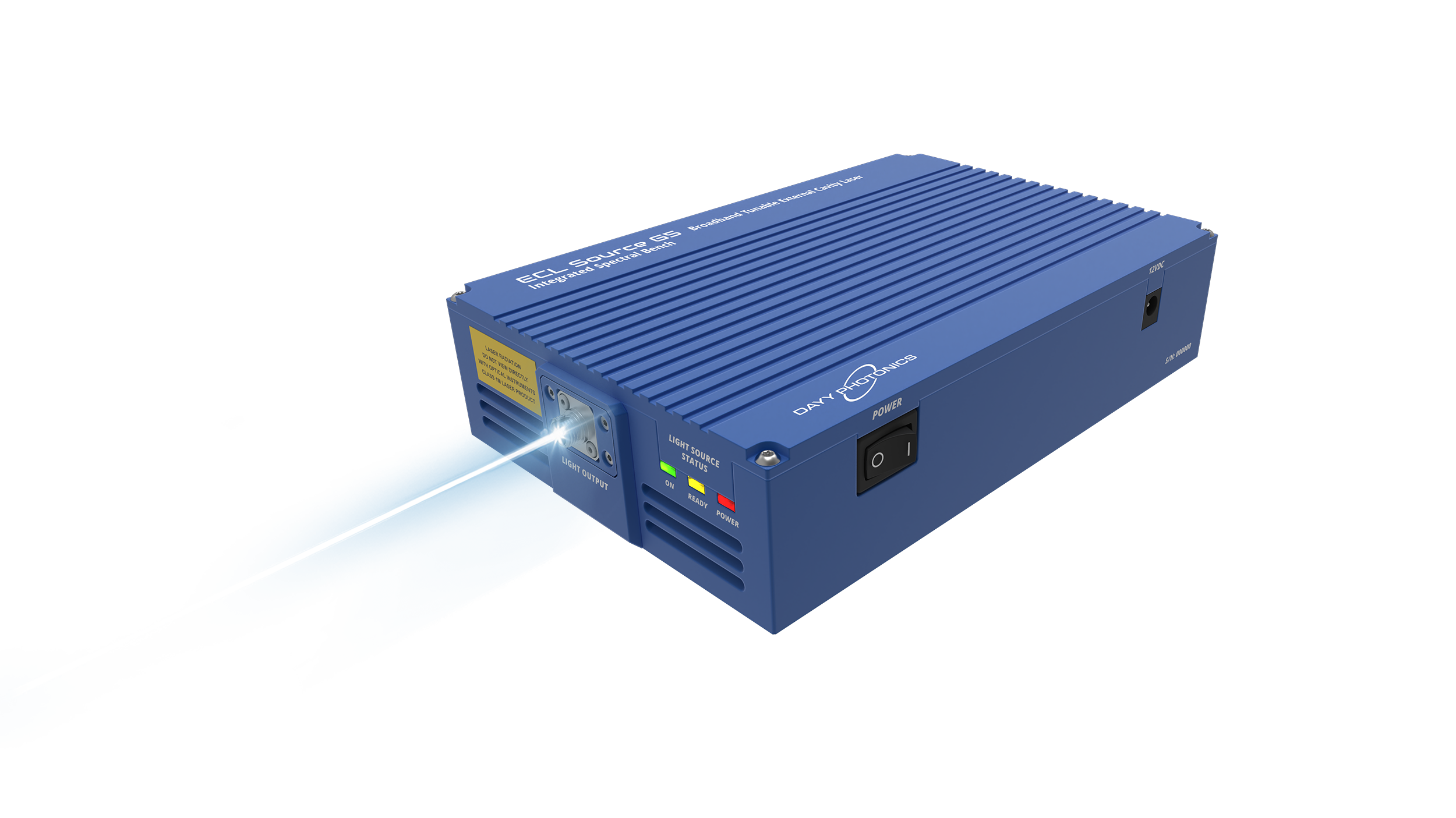
To learn more about our light source options for collimated output, contact DAYY Photonics to talk about the specialized needs in your application.
An AR coating reduces the reflection of the light from the surface. AR coatings are used to reduce reflection loss and hence improve transmission efficiency, while at the same time reducing stray light and ghost images.
Dayy Photonics offers fiber coupled light sources but also free space products with a collimated beam. We can customize our light sources to provide the desired beam diameters and minimum divergence angle.
A microscope objective is composed of a complex set of lenses and optics, and different objectives are designed for different imaging tasks. Capturing good images relies on choosing the correct objective.
Working distanceof 40x objective
3167 694 1124 - Instagram CustomEyes Cameras (@customeyescameras)We specialize in manufacturing durable high quality pipe ...
The objective is an essential part of the microscope and can greatly influence image quality. Objectives come with lots of information written on them, and most of it is written in code. But don’t worry; it’s easy to decipher.
3 products. Heart Ring Light RGB 20" Pro. Heart Ring Light RGB 20" Pro. Heart Ring Light RGB 20" Pro. Regular price $420.00.
Figure 4. The pencil appears bent or broken because the refractive indexes of water and glass are different than that of air.
Achromatic lenses are particularly good for collimating when a broad spectrum of wavelengths is present. They typically consist of two optical components cemented together, usually a positive low-index (crown) element and a negative high-index (flint) element.
When light rays with a specific orientation hit the surfaces of either parabolic or elliptical mirrors, they create a bundle of reflected rays. This bundle converges at a single point known as the focus.
Shop laser lights for stage or outdoor use. Professional lighting, projector laser ... ADJ Ani-Motion Red & Green ...
Advanced Illumination Brightfield/Darkfield LED Ring Lights can be used independently or simultaneously and are available with fixed intensity or strobed at ...
Sensor Connector, Micro-Change 120071 Series, M12, Plug, 4 Contacts, Pin, Straight Cable Mount. MOLEX. Order Code. 15M7973. Information ...
Each type of plano lens has its specific properties and applications, making them suitable for different optical needs. Plano lenses are typically a cost-effective option when your minimum divergence specification can be relaxed, such as systems that do not require the beam to stay collimated for long distances.
Working distanceformula
Magnification tells you the optical magnification the objective provides. The magnification you choose depends on what you want to see. The usefulness of magnification will be limited by your resolution. Making a big fuzzy blob of light even bigger won’t give you a better picture. Provided you have similar resolution at different magnifications, using higher magnification will allow you to see smaller things (such as organelles inside a cell) better. On the other hand, using a lower magnification will give you a better image of the big picture—such as a field of cells or interactions between cells.
The diagram below shows a beam of initial diameter x1 being shrunk to a final diameter of x2 and the distance between the two lenses is d. If we wanted to expand the beam, the plano-concave (negative focal length) lens would be placed first and have focal length f1, and the plano-convex lens would be placed second and have focal length f2.
A collimator lens system, composed of a set of lenses, can be employed to create a collimated beam. In this method, the light source is situated at one end of the system, and the lenses are arranged in a way that they refract and concentrate the light, resulting in a parallel beam. This technique is commonly utilized in laser diodes, telescopes, and other optical devices that necessitate a collimated beam.
Equipped with the dimmable function, the Minimalist LED Linear Wall Mounted Sconce Light Bar can modernize your living room, bedroom, or any other space.
Each objective is designed for a specific immersion medium, which is marked on the objective. The main types of immersion media are air, oil, and water. It is important that you never put air objectives in oil or other liquids. Doing this will make the person in charge of the microscope really angry! The main purpose of using different types of immersion media is to minimize the refractive index differences that are present in the space between the objective and the sample. This includes the substrate (i.e., glass coverslip) that the sample is on and the imaging medium (i.e., buffer) that the sample is in. Minimizing this difference will result in better image resolution.
An achromatic lens comes in a variety of configurations, most notably, positive, negative, triplet, and aspherized. It is important to note that it can be a doublet (two elements) or triplet (three elements); the number of elements is not related to the number of rays it can correct. In other words, an achromatic lens designed for visible wavelengths corrects for red and blue, independent of it being a doublet or triplet configuration. Below are diagrams outlining the four varieties of achromatic lenses.
Achromatic lenses provide users with the ability to regulate the field of view, collection efficiency, and spatial resolution of their setup. They also enable the configuration of illumination and collection angles, which is beneficial for sampling purposes.
What is a working distanceonamicroscope
AR coatings are applied via a series of layers adhered to the front and back of the lenses. These layers block certain wavelengths of light, helping to reduce reflection.
Light will travel through different types of materials at different rates. When light travels through one material (such as air) and into another (such as water), the light is refracted. It appears bent. For instance, when you put a pencil in a glass of water and view the glass from the side, the pencil will look bent. This is because air has a different refractive index than water.



 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500